
E-mail : info@mayer.cn
E-mail : info@mayer.cn
2025-07-14
In modern home renovations and public building water supply systems, stainless steel pipes have become the preferred choice for direct drinking water systems due to their excellent hygienic properties and durability. However, for ordinary consumers, the different grades of stainless steel materials can often be confusing. This article provides a detailed introduction to the commonly used materials for stainless steel drinking water pipes, helping you understand the differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel and how to make an informed choice based on actual needs.
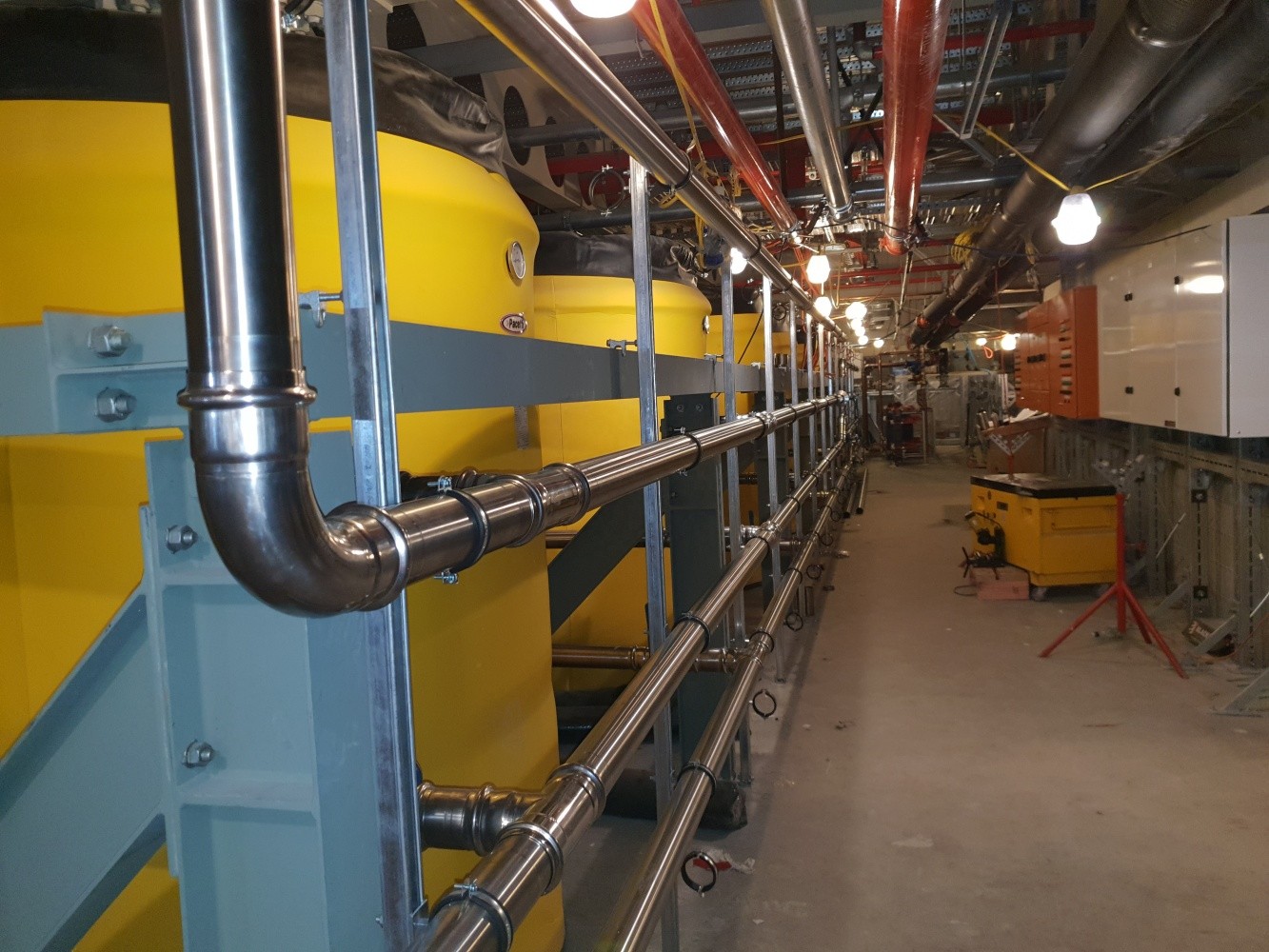

Stainless steel pipes are used in commercial areas
1. Why Stainless Steel Pipes Are Preferred for Drinking Water Systems
Traditional galvanized steel pipes are prone to rust, and plastic pipes may release harmful substances, making stainless steel pipes stand out in the field of direct drinking water. Stainless steel has extremely strong corrosion resistance, meaning it won’t produce rust contaminants that pollute water quality over long-term use. Its smooth surface prevents scaling and bacterial growth, and its high strength and long lifespan (typically over 50 years under normal use) make it ideal. Additionally, it is resistant to high temperatures and pressure, adapting to various water supply environments. These characteristics make stainless steel the ideal material for ensuring safe drinking water.
2. 304 Stainless Steel: The Mainstream Choice for Drinking Water Pipes
Food-grade 304 stainless steel (06Cr19Ni10) is currently the most widely used material in direct drinking water systems. It contains 18%-20% chromium and 8%-10.5% nickel, offering the following features:
Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Chromium forms a dense chromium oxide protective film on the surface, effectively resisting chloride ions and general corrosive agents in water.
Good Workability: Easy to weld and bend, making it suitable for manufacturing pipes and fittings of various specifications.
Cost-Effective: Compared to higher-grade 316 stainless steel, 304 is more affordable while offering strong performance.
China’s "GB/T 29038-2012 Technical Specification for Thin-Walled Stainless Steel Pipes" explicitly lists 304 as a recommended material for drinking water pipes. In everyday environments such as homes, schools, and office buildings where chloride ion content is not high, 304 stainless steel fully meets long-term safe water transportation requirements.
Stainless steel pipes are used in residential areas
3. 316 Stainless Steel: The Premium Choice for Demanding Environments
316 stainless steel (06Cr17Ni12Mo2) contains an additional 2%-3% molybdenum compared to 304, further enhancing its properties:
Stronger Corrosion Resistance: Molybdenum significantly improves resistance to chlorides, seawater, and acidic media.
Suitable for Harsh Environments: Performs exceptionally well in coastal areas, high-salinity water, or specialized medical water systems.
Longer Lifespan: In corrosive environments, its lifespan can be 30% longer than 304.
However, 316 stainless steel typically costs 20%-30% more than 304, which may be an unnecessary expense for standard municipal water systems. Therefore, the choice should be based on actual water quality conditions rather than blindly opting for a higher-grade material.
4. How to Identify High-Quality Stainless Steel Pipes
Some unscrupulous suppliers may use non-food-grade stainless steel (such as 201) to impersonate 304/316. Consumers can make a preliminary judgment using the following methods:
Check Markings: Legitimate products are laser-marked with material information such as "SUS304" or "06Cr19Ni10."
Testing Solution: Special stainless steel testing solutions can distinguish different materials based on color changes.
Request Reports: Ask suppliers for material test reports to confirm chromium, nickel, and molybdenum content meets standards.
Inspect Surface Quality: High-quality stainless steel pipes have smooth, uniform inner and outer walls without defects like pits or cracks.

Stainless steel pipes are used in buildings

Stainless steel pipe and fitting manufacturer - Guangzhou Mayer Corp., Ltd.
5. Material Selection Advice and Considerations
Choose Based on Water Quality: 304 is sufficient for standard tap water; 316 is recommended for coastal or high-chloride environments.
Pay Attention to Wall Thickness: Drinking water pipes should have a wall thickness of at least 0.6mm, with thicker walls needed for pressure-bearing pipes.
Use Matching Fittings: Avoid electrochemical corrosion by using fittings made of the same material.
Opt for Reputable Brands: Well-known brands offer better material purity and manufacturing quality control.
As awareness of drinking water safety grows, stainless steel pipes are gradually replacing traditional materials. Understanding the differences between 304 and 316 and making a rational choice based on actual conditions ensures safe drinking water while avoiding unnecessary costs. Before purchasing, consult a professional plumbing engineer and test local water quality to determine the most cost-effective piping solution. Remember, the best choice is the one that fits your needs—there’s no need to blindly opt for the highest grade when a more suitable alternative is available.