
E-mail : info@mayer.cn
E-mail : info@mayer.cn
2025-09-28
304 and 316L are the most common grades of austenitic stainless steel. Their excellent corrosion resistance, workability, and strength make them indispensable across numerous industries.
So, what are the specific application fields for 304/316L stainless steel pipes and fittings? Let's explore them one by one.
1. Food and Beverage Industry (Food Grade)
Processing Equipment: Pipelines for transporting beverages like milk, beer, wine, and juices.
Brewing and Distilling: Fermentation tanks, mash tuns, distillation columns, and product transfer lines.
Dairy Processing: Pipes for conveying milk, cream, and other dairy products.
Sanitary/Hygienic Systems: High-purity transfer lines where exceptional cleanliness and sterilization (CIP - Clean-in-Place) are critical.
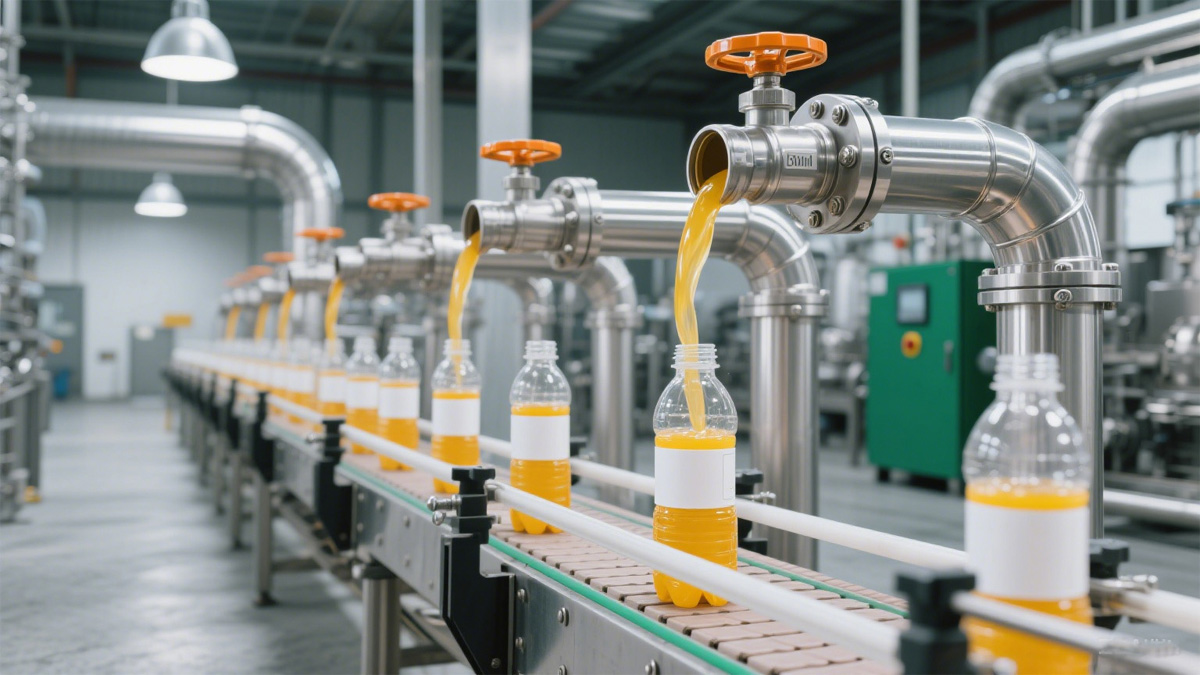

Stainless Steel Pipe of Beverage Industry
2. Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Industries
High-Purity Water Systems: For Water for Injection (WFI) and purified water distribution systems.
Process Piping: For transferring Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and process fluids.
Bioprocessing: Fermenters, bioreactors, and filtration systems requiring stringent hygienic standards and corrosion resistance.
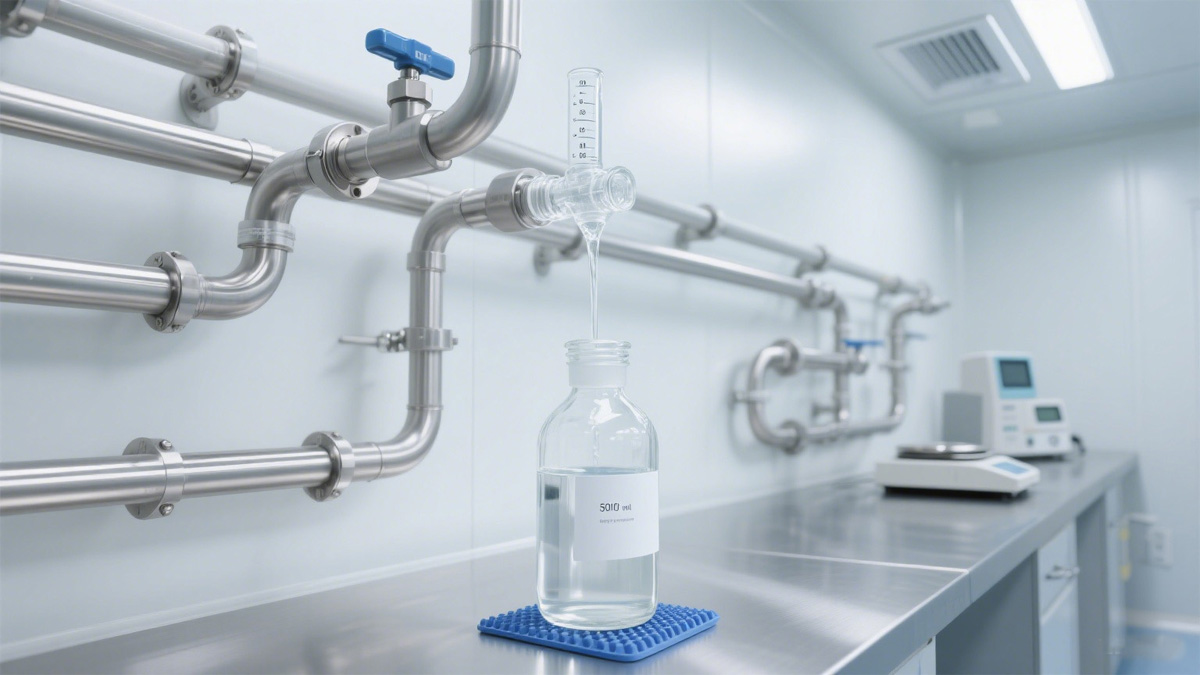

Stainless Steel Pipe and Fitting of Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Industries
3. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
Chemical Processing: Transporting various chemicals, solvents, and acids (316L is often preferred due to its superior resistance to chlorides and acids).
Oil and Gas: Piping on offshore platforms, instrument tubing, and lines in corrosive environments.
Refineries: Piping for corrosive intermediates and products.
4. Architecture and Construction (A&D)
Handrails and Railings: For both interior and exterior applications, offering aesthetics and durability.
Structural Members: Hollow Structural Sections (HSS) used in modern buildings and curtain walls.
Water Features and Sculptures: For decorative elements in landscaping and architecture.
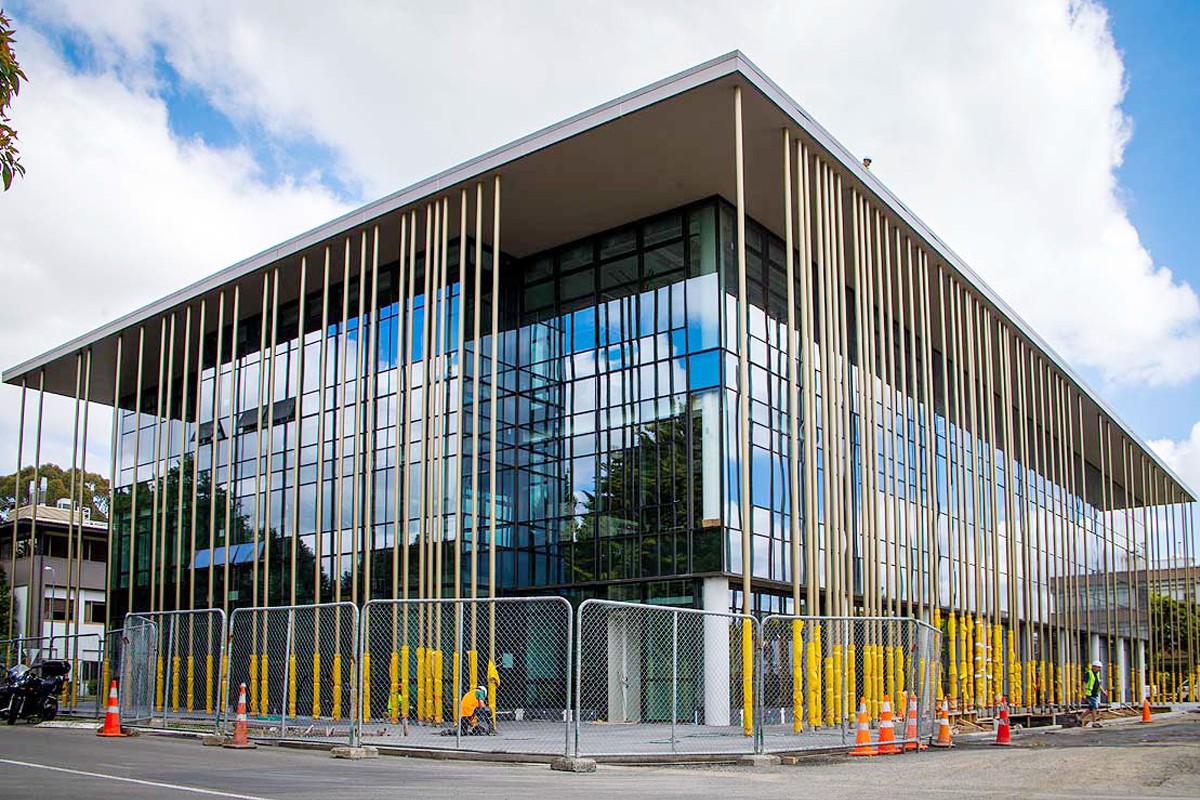

Stainless Steel Pipe of Handrails and Railings
5. Water Treatment and Wastewater
Potable Water Systems: Pipes, conduits, and supply lines within buildings and municipal systems.
Wastewater Treatment: Equipment and piping exposed to corrosive chemicals and atmospheres.
Desalination Plants: 316L is widely used due to its excellent resistance to saline water corrosion.
Stainless Steel Pipe of Potable Water Systems
6. Marine and Offshore Engineering
Ship Fittings: Bow rails, guardrails, ladders, and cleats.
Marine Applications: Piping, hydraulic lines, and exhaust systems on ships and offshore platforms (316L is crucial for seawater environments).
7. Automotive Industry
Exhaust Systems: Mufflers, tailpipes, and catalytic converter housings (particularly Grade 304).
Fuel Lines: For certain fuel types and brake lines.
Structural Components: In high-end or specialty vehicles.
8. Heat Exchangers and Condensers
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers: Tubes and shells for heating or cooling process fluids.
Condensers: Used in power plants, HVAC systems, and refrigeration units.
9. Pulp and Paper Industry
Bleach Plants: Process equipment and piping handling corrosive bleaching chemicals (often specified as 316L).
10. Energy and Power Generation
Nuclear Power: Certain non-critical components and auxiliary systems.
Fossil Fuel Power Plants: Piping for feedwater, condensate, and other systems.
Solar Power: Structural components and piping in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants.
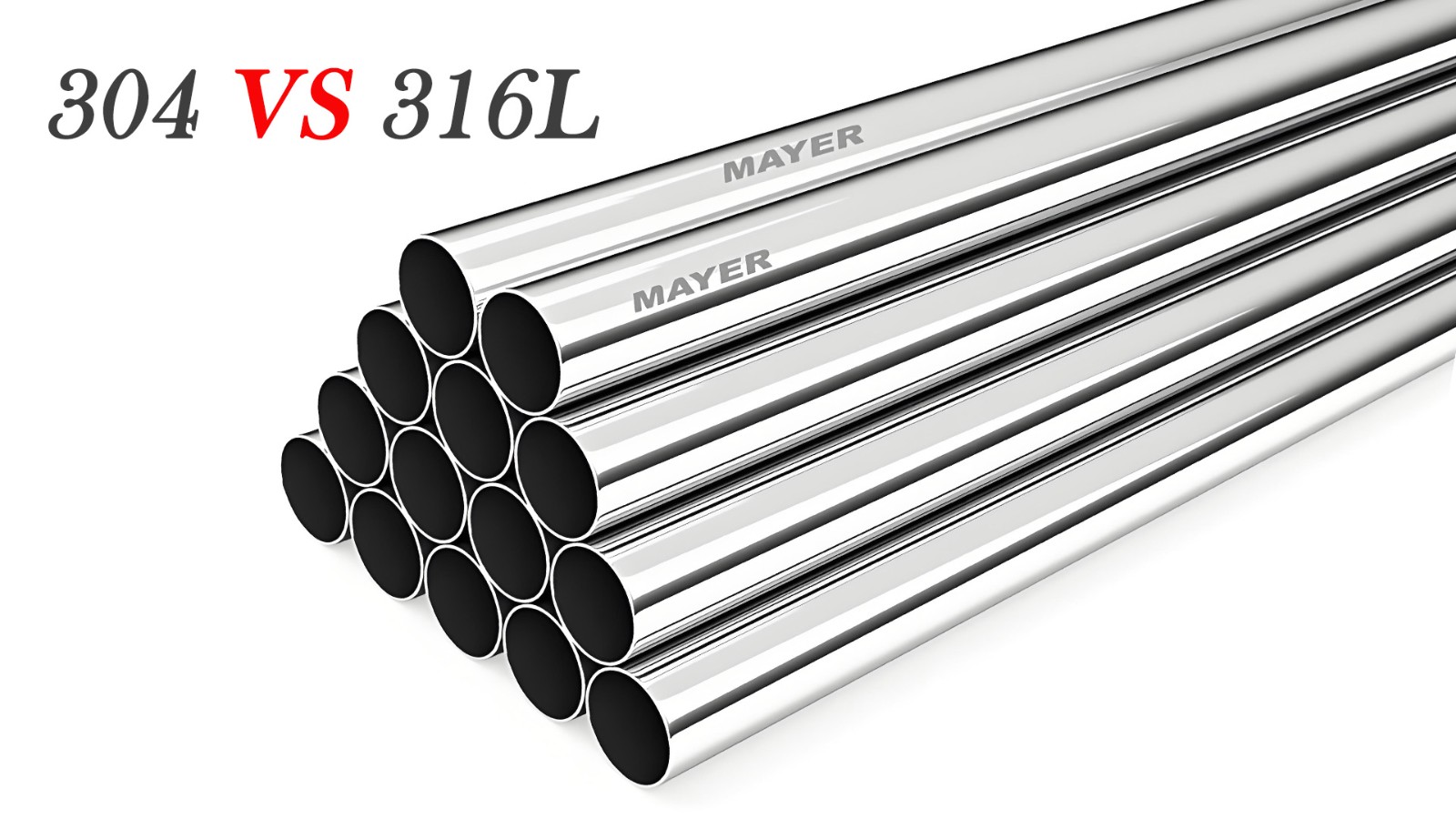

304 Stainless Steel Pipe VS 316L Stainless Steel Pipe
Key Differences in Application: 304 vs. 316L
* Grade 304 (Standard Austenitic): The most versatile and commonly used grade. Suitable for most applications involving fresh water, mild acids, and foodstuffs. Not recommended for chloride-rich environments (e.g., coastal areas, de-icing salts) as it is susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion.
* Grade 316L (Marine Grade / Molybdenum-Enhanced): Contains Molybdenum (Mo), which significantly enhances its resistance to chlorides, acidic compounds, and pitting. The "L" denotes low carbon content, providing superior resistance to sensitization (carbide precipitation) during welding.
Use 316L when: For saline water environments, chemical processing involving chlorides or sulfuric acid, pharmaceutical plants, coastal architecture, and any harsh environment where 304 would be inadequate.